Early Stage of Tooth Decay and Its Treatment
Tooth decay is when your teeth become damaged, which can lead to cavities, dental abscesses, and even tooth loss. It's brought on by the action of specific bacteria that live in dental plaque.
Plaque bacteria have the ability to convert sugars in your food into acids. These acids can destroy your teeth if plaque is allowed to build up over time and this is why maintaining good dental hygiene is so important in avoiding tooth decay.
There are different stages of tooth decay. We'll go over each of these stages in detail below, as well as how to treat tooth decay and how to avoid it.
Early Stages of tooth decay
Dental plaque plays a vital role in tooth decay. Plaque is a whitish, sticky coating that forms on your teeth's surfaces. Bacteria, food particles, and saliva make up this substance.
Plaque can build up on your teeth if you don't brush them regularly. It can also harden with time, resulting in tartar formation. Tartar can assist to preserve bacteria even more, making them more difficult to eliminate.
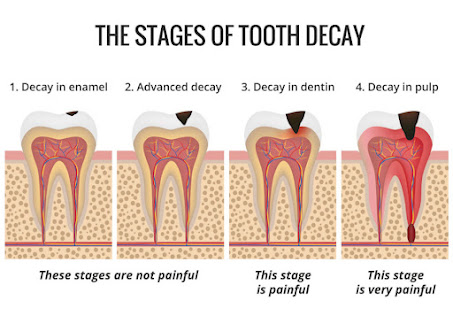
Tooth decay can be classified into five stages. Let's take a closer look at each of them.
Stage 1: Initial demineralization
Enamel is a type of tissue that makes up the outer covering of your teeth. The toughest tissue in your body is enamel, which is largely made up of minerals. The enamel, on the other hand, begins to lose these minerals as a tooth is exposed to acids produced by plaque bacteria.
You may see a white spot on one of your teeth if this happens. The loss of minerals in this area is the first indicator of tooth decay.
Stage 2: Enamel decay
Enamel will continue to deteriorate if tooth decay is allowed to continue. A white spot on a tooth may deepen to a brownish tone over time. Small holes in your teeth called cavities, or dental caries, can form as enamel weakens. Your dentist will need to fix any cavities..
Stage 3: Dentin decay
The dentin is the tissue beneath the enamel. It's softer than enamel, making it more vulnerable to acid damage. As a result, tooth decay progresses more quickly once it reaches the dentin.
Dentin also contains tubes that connect to the tooth's nerves. As a result, when the dentin is impacted by tooth decay, you may notice sensitivity. This is most noticeable when eating or drinking hot or cold meals or beverages.
Stage 4: Pulp damage
The pulp is your tooth's innermost layer. It houses the nerves and blood vessels that keep the tooth in good shape. The pulp's nerves also supply sensation to the tooth.
When the pulp is damaged, it might become inflamed and swell. Because the tooth's surrounding tissues are unable to expand to accommodate the enlargement, pressure may be imposed on the nerves. This can result in discomfort.
Stage 5: Abscess
Bacteria can infiltrate the pulp as tooth decay progresses, causing an infection. An abscess is a pocket of pus that forms at the bottom of your tooth as a result of increased inflammation in the tooth.
Abscesses in the teeth can cause excruciating discomfort that can spread to the jaw. Swelling of the gums, face, or jaw, fever, and swollen lymph nodes in the neck are all possible signs.
A tooth abscess should be treated as soon as possible since the infection can spread to your jaw bones and other parts of your head and neck. The damaged tooth may need to be removed in some circumstances.
Tooth decay in children
Tooth decay can also affect children. Tooth decay is one of the most frequent chronic pediatric illnesses in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)Trusted Source.
In addition, children are more likely than adults to develop dental decay. This is due to the fact that a child's baby teeth have thinner and more sensitive enamel than adult teeth.
Tooth decay occurs when bacteria break down sugars into acids, which harm tooth structures, much as it does in humans. As a result, it's critical to ensure that your child doesn't ingest excessive amounts of sugary foods or beverages, and that their teeth are washed on a regular basis.
Even while baby teeth eventually fall out, it is still important to keep them healthy. Baby teeth are necessary for chewing and speaking, but they also serve as placeholders for adult teeth. Adult teeth may not come in properly if baby teeth are lost too early due to decay.
Treatments For Early Stage Tooth Decay
Depending on the stage of tooth decay, several treatments may be prescribed. Let's look at the various treatment choices based on how far tooth decay has progressed.
Initial demineralization
Before more severe damage occurs, this early stage of tooth decay can be corrected. This can be accomplished by fluoridating the teeth.
Fluoride treatments are available at your dentist's office. It's frequently administered to your teeth as a gel or varnish. Fluoride helps to strengthen enamel, making it more resistant to plaque bacteria's acids.
Fluoride is also included in several toothpastes and is frequently found in tap water. Fluorinated water is consumed by about 74 percent of Americans who acquire their tap water from a community water system.
Enamel decay
Cavities are common when tooth deterioration reaches this stage. Cavities are treated by fillings.
Before placing a filling, your dentist will use a tool to remove any decayed regions. They'll then use a material like resin, ceramic, or dental amalgam to fill the hole. The hue of this substance is usually the same as your teeth.
Dentin decay
Because dentin is weaker than enamel, deterioration advances more quickly at this stage. Dentin decay can be treated with a filling if caught early enough. In more advanced situations, a crown may be necessary.
A crown is a cap that goes over the top of your tooth, above the gums (also called the crown of the tooth). Before the crown is fitted, the decaying region is removed. To ensure that the crown fits properly on your tooth, some healthy tooth tissue may be removed as well.
Pulp damage
A root canal is often required when tooth decay has reached the pulp. The injured pulp is removed during a root canal procedure. After that, the tooth cavity is cleansed and filled. On the afflicted tooth, a crown is put.
Abscess
Your dentist would most likely perform a root canal to remove the infection and seal the tooth if an abscess has formed in your tooth. In severe circumstances, the tooth may need to be extracted entirely.
Antibiotics may be prescribed to aid in the treatment of an abscess. These are antibacterial drugs.
Preventions For Early Stage Tooth Decay
The importance of good oral hygiene in preventing tooth decay cannot be overstated. The following are some tactics you may use to assist prevent tooth decay from causing damage to your teeth.
Visit your dentist on a regular basis: Your dentist can assist you in detecting and treating tooth decay before it progresses. Make an appointment with your dentist for routine tooth cleanings and oral exams on a regular basis.
Brush your teeth: Brushing your teeth at least twice a day is generally suggested. After meals and Trusted Source Use a fluorinated toothpaste if possible.
Limit sweets: Try to avoid foods or drinks that contain a lot of sugar. Candies, cookies, and soft drinks are just a few examples.
Drink tap water: Fluoride is found in most tap water, which can help keep your enamel strong and prevent decay.
Avoid snacking between meals: Snacking between meals can provide bacteria in your mouth with even more sugars to convert into acids.
Inquire about sealants: Sealants are a thin plastic coating that is put to the backs of your teeth (molars). Molars are necessary for chewing, but they can also retain food particles in their grooves. A sealant is applied on the molar's surface to prevent this from happening.
When to see a dentist
You may not notice any signs if your tooth decay is in its early stages. This is why it's critical to see your dentist on a frequent basis. Early stages of tooth decay can be identified and treated by your dentist before they progress.
If you have tooth sensitivity, discomfort, or swelling in or around your mouth, make an appointment with your dentist. These could be symptoms of advanced tooth decay or another dental problem that needs to be addressed.

Post a Comment